
The Burrowing Owl
A Burrowing Owl is a fun bird to see while bird watching. Below are some tips to help you identify Burrowing Owls. We have also put together a list of fun Burrowing Owl t-shirts, Burrowing Owl bird patches, bird houses, bird feeders, binoculars, stickers and other fun bird watching items.
About Burrowing Owls
These owls were commonly referred to as howdy birds by cowboys. This is because they seemed to greet them form the entrance of their burrows. They are active during the day and often hunt small animals on the ground. Burrowing owls live in underground burrows that they’ve either dug themselves or abandoned by tortoise or squirrels. Some of their distinctive features include:
Description and Identification
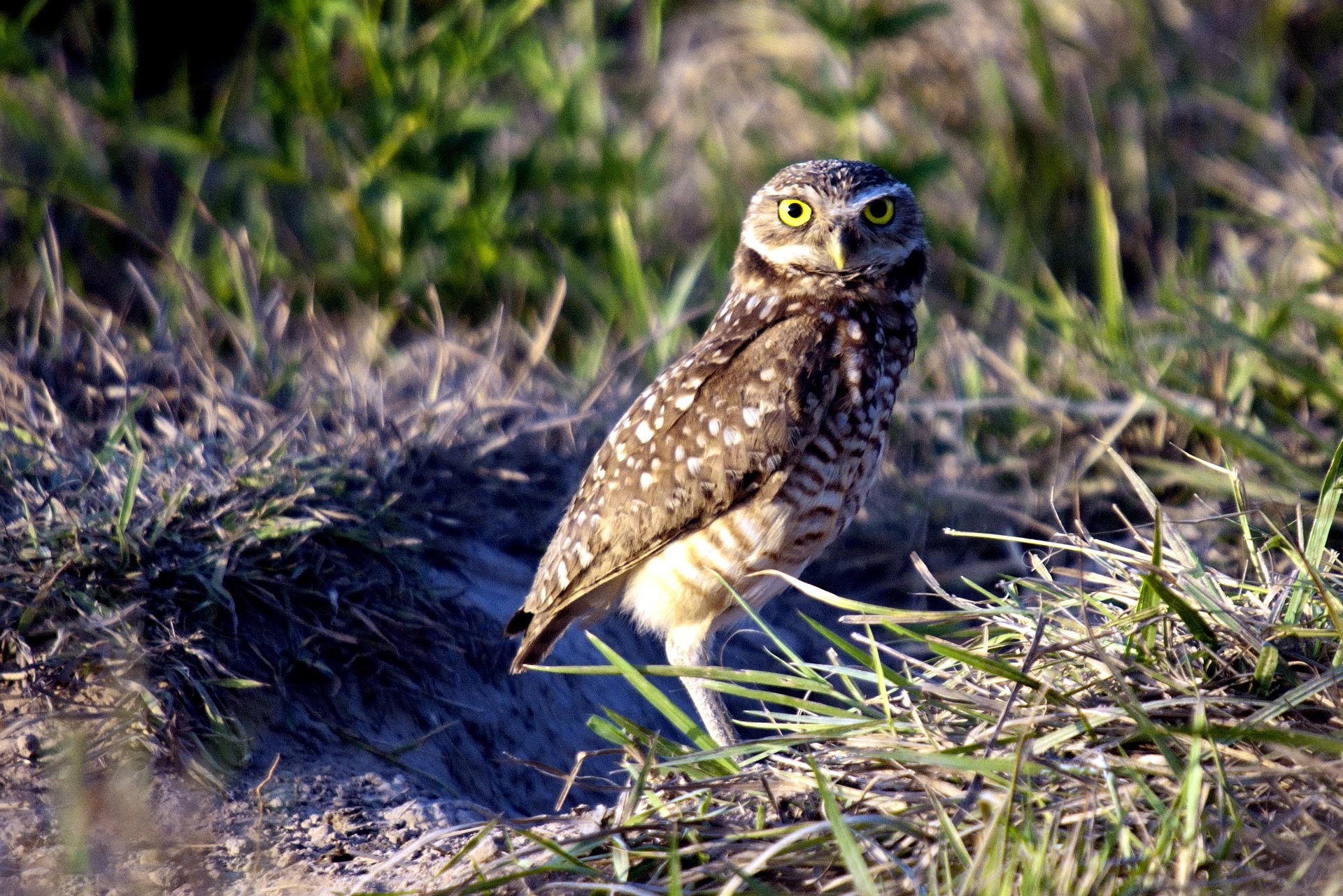
Along with bright eyes, Burrowing Owls have dark yellow or gray beaks. They have prominent white eyebrows and a white chin patch, which they expand and display during certain behaviors. The adult Burrowing Owls have brown heads and wings with white spotting. The chest and abdomen of the owls are white with variable brown spotting or barring. The juveniles, though similar in appearance, lack most of the white spotting and brown barring. They have a buff bar across the upper wing, and their breast may be buff-colored. Both the adults and juveniles have grayish legs longer than those of other owls.
Burrowing Owl Color Pattern
They are primarily brown and lack ear tufts. They have a white throat and chin and their eyes are bright yellow. Juveniles are brown but less mottled than adults. They have buffy-yellow wing patch and underparts.
Burrowing Owl Size
Burrowing owls are larger and bulkier than an American Robin but dwarfed by a Western Screech-Owl. They are long-legged, have short tails and their heads are round with no ear tufts.
The relative size of both sexes
- Length range: 7.5-9.8 in (19-25 cm)
- Weight: 5.3 oz (150 g)
- Wingspan range: 21.6 in (55 cm)

Burrowing Owl Behavior
They primarily spend most of their time on low perches or on the ground. On the ground, they hunt for small animals and insects. These owls are most active during the day. They use various tactics to catch prey. They can either run on the ground, then catching prey with their talons, hovering around fields or surprising prey from a perch.
Burrowing Owls Food
While hunting, Burrowing Owls wait on a perch until they spot prey. The owls primarily consume invertebrates and small vertebrates, including birds, lizards, and mammals. Invertebrates constitute the majority of food items, whereas vertebrates make up the majority of the diet by mass. These birds commonly hunt crickets, grasshoppers, moths, beetles, mice, voles, and shrews. Burrowing Owls mainly eat large insects and small rodents, and they often live close to ground squirrels. They also prey on dragonflies, small weasels, young rabbits, bats, salamanders, scorpions, ground squirrels, songbirds, waterbirds, baby ducks, giant water bugs, and even young burrowing owls. Female Burrowing Owls catch more insects, mostly during the day.
Their diet mostly comprises of small animals and insects. In summer they feed on large insects such as grasshoppers, crickets, beetles, scorpions, centipedes, and other arthropods. For the rest of the seasons, they can feed on small animals such as mice, voles, some small birds and squirrels.
Burrowing Owl Habitat
Burrowing Owls are usually found in open, treeless areas with low and sparse vegetation. They can be seen in grasslands, deserts, and steppe environments; on golf courses, pastures, agricultural fields, airport medians, and road barriers. The owls are frequently observed along the banks of irrigation canals. They have been often associated with high densities of burrowing mammals, such as prairie dogs, ground squirrels, and tortoises. The breeding Burrowing Owls pair stay near a dedicated nesting burrow, whereas wintering owls may move and may roost in tufts of vegetation rather than in burrows.
Burrowing owls are common in areas that are treeless with less vegetation, preferably gently sloping terrains. They can be found in cemeteries, deserts, golf courses and urban vacant lots. They are associated with ground squirrels and prairie dogs since they nest in their burrows.
Range and Migration
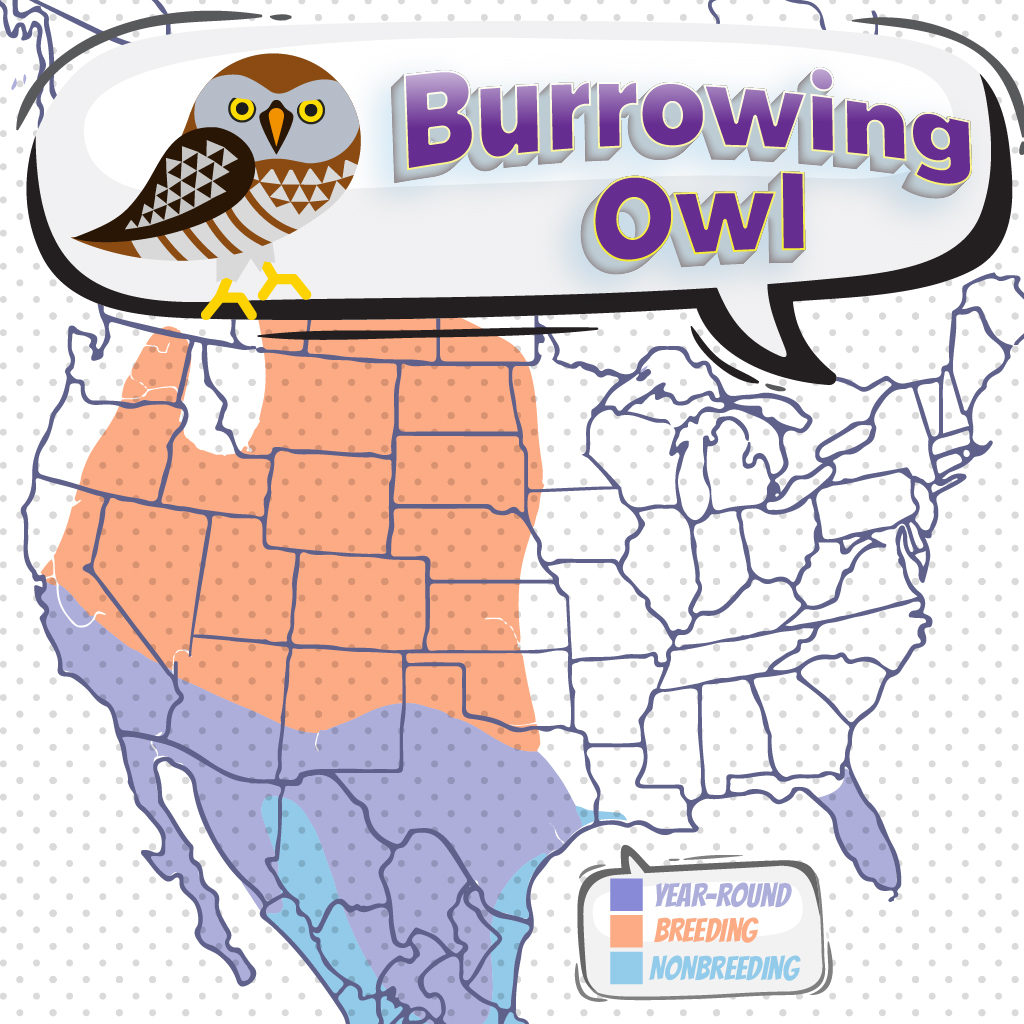
Burrowing Owls are small-legged owls who are found throughout open landscapes of North and South America. They can be seen year-round in Florida, Mexico, and parts of South America, except the Amazon rain forest. The owls breed from southern Alberta eastward to southern Manitoba, southward into Mexico. They are also residents in Florida and into the Caribbean, and throughout South America. In South America, the birds are patchy in the northwest and through the Andes. They are year-round residents in most of their range. Most of the Burrowing Owls spend their winter in southern Mexico and Central America. The owls that breed in Washington migrate south along the coast and winter in California.
Nesting
Burrowing Owls form monogamous pair bonds during the nesting season. The nesting season begins in late March or April in North America. Pair of Burrowing Owls will sometimes best in loose colonies. They also nest in shallow, underground, human-made structures that have easy access to the surface. The owls tend to use areas with a high density of surrounding burrows. The preferred sites have loose soil, a bit of elevation to avoid flooding, and nearby lookouts, such as dirt mounds, bushes, fence posts, and road signs. The female owls incubate their eggs while the male owls bring food.
Burrowing Owl Lifecycle
The females typically lay 7-10 eggs and incubate them for 28-30 days. The males are tasked with feeding the females during incubation. The female feeds the young ones and they leave the nest after 6 weeks. They have a lifespan of 6-8 years.
Ornithology
Bird Watching Academy & Camp Subscription Boxes
At Bird Watching Academy & Camp we help kids, youth, and adults get excited and involved in bird watching. We have several monthly subscription boxes that you can subscribe to. Our monthly subscription boxes help kids, youth, and adults learn about birds, bird watching, and bird conservation.
Bird Watching Binoculars for Identifying Burrowing Owls
The most common types of bird watching binoculars for viewing Burrowing Owls are 8×21 binoculars and 10×42 binoculars. Bird Watching Academy & Camp sells really nice 8×21 binoculars and 10×42 binoculars. You can view and purchase them here.
Burrowing Owl T-shirts
If you love the Burrowing Owl you should purchase a Bird Watching Academy & Camp T-shirt. To help support bird conservation we donate 10 percent to bird conservation activities.
Burrowing Owl Iron On Patches
Kids, Youth, and Adults love to collect our Bird Watching Academy & Camp iron on patches. Our bird watching patches help you keep track of the birds you have seen an identified. You can also display the patches on our Bird Watching Academy & Camp banners.
The Burrowing Owl is a great iron on patch to start your collection with. The patches are durable and can be sewn on or ironed on to just about anything.
Burrowing Owl Stickers
Stickers are a great way for you to display your love for bird watching and the Burrowing Owl. We sell a monthly subscription sticker pack. The sticker packs have 12 bird stickers. These sticker packs will help your kids learn new birds every month.
Bird Feeders For Burrowing Owl
There are many types of bird feeders. Here are our favorite bird feeders for your backyard. We use all of these bird feeders currently. Kids will have a great time watching birds eat at these bird feeders. Using this collection of bird feeders will provide a wide variety and many types of birds.
Best Bird Houses for Burrowing Owl
There are many types of bird houses. Building a bird house is always fun but can be frustrating. These 4 bird houses have become our favorites. Getting a bird house for kids to watch birds grow is always fun. We spent a little extra money on these bird houses but they have been worth the higher price and look great.









